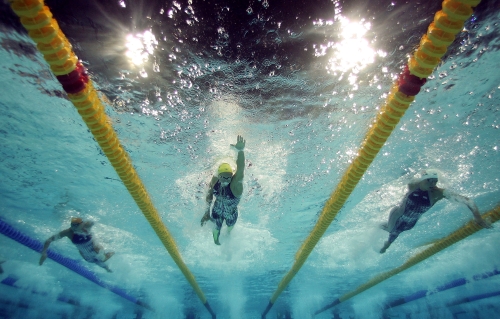For Halloween, a friend had a helium balloon that he was playing with. He would inhale a little bit of helium and then talk in a high, squeaky voice. I wondered why this happens and researched it. Helium is less dense than air. Helium's speed of sound is also 3 times faster than that of air, meaning that helium's wavelengths have a higher frequency. Because of these two factors, the speed of sound in the voice is increased when helium is inhaled. This increases in wavelength increases the pitch of the resonating frequencies of the vocal tract.
One could lower the pitch of the voice by inhaling a gas that is more dense than air. Denser gases include sulfur hexafluoride and xenon.
Monday, October 31, 2011
Sunday, October 30, 2011
Silent flight in owls
As I was thinking about birds in flight, I thought about owls. Owls have the advantage that they can fly silently. The primary reason for their silent flight is an adaptation they have in their wings. In most birds, air creates a sound when it rushes over the top part of the wing. The rushing wind creates turbulence, thus creating the sound. Owls have comb-like feathers along the edge of their primary feathers. These comb-like feathers reduce the turbulence on the wings by breaking it into "micro-turbulences". This decreases the sound made by turbulence, giving the owls a more silent flight.
Another factor is that owls have big and rounded wings. This enables them to fly buoyantly and without too much effort, meaning that they don't have to flap their wings as much as regular birds. Not flapping their wings so much also decreases the noise in their flight.
Another factor is that owls have big and rounded wings. This enables them to fly buoyantly and without too much effort, meaning that they don't have to flap their wings as much as regular birds. Not flapping their wings so much also decreases the noise in their flight.
Saturday, October 29, 2011
Birds in flight
My friend showed me this amazing video of an owl in flight. I became mindful of bird's characteristics that enables them to fly. Their wings are the biggest reason. The shape of a bird's wings is called an airfoil. Wind will flow over the wing and under the wing. The phenomenon that will enable the bird to lift is that the pressure of the air moving over the wing is less than the pressure of the air moving under the wing. Thrust is also present in bird flight; it is created when the bird flaps its wings to crete speed.
Friday, October 28, 2011
Wind testing in race cars
Wind tunnel testing can also be useful when designing race cars. Drag forces is something that can be analyzed in this kind of testing, and in the case of a race car, these analysis can help to design a faster car. Lift can be reduced in the car by changing the frontal area of it. Wind testing can show how much drag force is acting on the car, therefore engineers can change the frontal part of the car to reduce these drag forces and make the race car faster and more efficient. This is one of the main reasons why the front part of a race car has a different structure than the front part of a regular car.
Thursday, October 27, 2011
Laminar flow in wind tunnels
I was thinking about a car undergoing testing in a wind tunnel, and became aware that the wind going in this experiment has mostly laminar flow, meaning that the fluid (the air) is flowing along a smooth path, and its particles never cross each other.
Wednesday, October 26, 2011
Preventing sinking with snowshoes
The winter is approaching fast, and my thoughts went to colder weather and snow. I started thinking about the different clothing and equipment that one would use in the snow. I thought about snowshoes, and how they help when walking through areas where there is a lot of snow, especially soft snow. They prevent you from sinking in the soft snow because they "spread" the downward force that our bodies exert on the snow by increasing the area on which the force is acting on. This reduces the pressure on the snow's surface and enables people to walk in snow easier without having to tread through it.
Tuesday, October 25, 2011
Blue sky
Today was a clear day, with a blue sky. I became mindful of why the sky is blue. When light waves move through the atmosphere, most of the longer waves pass through it. But the colors with shorter wavelengths, like the color blue are absorbed by gas molecules. This absorbed blue light is then radiated and scattered in different directions, giving the sky its beautiful blue color.
Monday, October 24, 2011
Bad hair day
Today, after I took off my sweater, my hair stood up on end. This was because of static electricity in the dry air, and the rubbing of the material of the sweater. With the rubbing, electrons transferred from the sweater (which was probably made from a material that is an insulator) to my hair. The hair is filled with electrons, which are repelling each other. As they repel each other, hair strands will try to move away from each other, and the way they do it is by standing up and away from each other.
Sunday, October 23, 2011
Electric shock
We were in the middle of practice picking up tennis balls with plastic tubes. When I put the balls in our metal baskets, I got an electrical shock. This is because I had extra electrons in my body when I touched the metal. There are many factors that come into play here. First off: the weather. Winter is approaching, and the air becomes more dry during the winter. The dryness in the air prevents the electrons from moving away from our bodies, makings us build up static charges. Second, the plastic tubes. Plastic is an insulator, meaning it doesn't hold electrons well. When I was touching the tube, electrons moved from the tube to my hands, giving me static charges. When I touched the metal (which is a conductor), the electrons moved from my body to the metal basket, creating the electric shock.
Saturday, October 22, 2011
Floating bubbles
My sister showed me an interesting experiment that was displayed in her science fair today. In a glass jar, bicarbonate and vinegar are mixed, creating a chemical reaction in which carbon dioxide is released. Soap bubbles are then released into the jar. These bubbles will float in the jar, because the bubbles have air inside of them, while they are surrounded by carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is more dense than air, which is what makes the bubbles float.
Friday, October 21, 2011
Headaches due to pressure gradients
I picked up my friend from Germany at the airport today and he told me that he was suffering from a big headache due to the flight. I explained to him that the reason behind this is because of the changes in pressure when you're flying. Behind our eardrums, there is an air space. If the pressure outside of the ear isn't the same as inside of it, the eardrum bends inward or outward, causing your head to hurt.
Thursday, October 20, 2011
Pressures in a plane
Today, my friend told me about an experience she had when flying. She had bought a bag with coffee beans from Starbucks before she got on the plane. She put it inside her suitcase, which travels in the bottom of the plane. When she arrived to Bulgaria and got the bag out of her suitcase, the coffee bag was "stuck" to the coffee beans. All the air had left the bag. This happened because of the pressure gradient in the plane. Pressure at such a high altitude is lower than pressure at sea level.
Wednesday, October 19, 2011
Cup&String Telephone
My little cousin was very excited to tell me that they had constructed a telephone artifact made out of cups and string. I remembered that I used to play with this too when I was young, and I thought about how it works. When you talk into your end of the "phone" (the cup), the sound waves hit the cup, make the cup vibrate, which then travel through the tight string by pulling it back and forth. The waves arrive into the other end of the phone, where they make the other cup vibrate just like the first cup did. The tighter the string, the better it carries the sound to the other cup.
Tuesday, October 18, 2011
Hot air balloon
Today, I was watching the move "Up", and I was mindful of how a hot air balloon works. The reason why it is able to move up and take people along for the ride is because of the hot air that is applied to the inside of the balloon (it is also known as the "envelope"). The hot air makes it buoyant because it makes it have a lower density than the colder air around it, (warmer air rises over colder air). The balloon doesn't have to be closed at the bottom because the air at the bottom of it has the same pressure as the surrounding air.
The balloon can be manipulated to move up and down. To make it rise, the hot flame is opened (the bigger the flame, the faster it moves up). To make it come down, a "valve" at the top of the envelope is opened to release the hot air inside the balloon, making it descend.
The balloon can be manipulated to move up and down. To make it rise, the hot flame is opened (the bigger the flame, the faster it moves up). To make it come down, a "valve" at the top of the envelope is opened to release the hot air inside the balloon, making it descend.
Monday, October 17, 2011
The attack of the shower curtain
When I turned the water on to shower today, the shower curtain kept sticking to me. I wondered why this happened, and found out that there a few explanations for it. When the showered is turned on, and the fluid accelerated, the pressure around it drops. Meanwhile, the pressure outside the shower curtain remains the same. This pressure gradient makes the curtain move inwards.
Another explanation is that when the shower sprays, the air inside turns into a vortex, and the pressure at the center of this vortex has a lower pressure, like the eye of a hurricane. This low pressure could be what sucks the curtain inwards.
Another explanation is that when the shower sprays, the air inside turns into a vortex, and the pressure at the center of this vortex has a lower pressure, like the eye of a hurricane. This low pressure could be what sucks the curtain inwards.
Sunday, October 16, 2011
Neutrinos traveling faster than speed of light
Today, I read an article stating that scientists may have found particles traveling faster than the speed of light. Scientists pumped "neutrinos" (neutral particles that are able to go through matter without being affected by it) from Geneva to Gran Sasso in Italy. The particles passed through water, air, and rock; and they traveled 60nanoseconds faster than what the speed of light would have traveled.
Scientists are quite positive of their results, but continue to run tests. If this is confirmed, then Einstein's theory of relativity would be considered invalid.
Scientists are quite positive of their results, but continue to run tests. If this is confirmed, then Einstein's theory of relativity would be considered invalid.
Saturday, October 15, 2011
Rainbows
Today, I was mindful that after a rainy day, we sometimes see beautiful rainbows in the sky. This happens when the sun's rays passes through water droplets. The ray of light is refracted as it enters the drop, reflected off the back of the drop, and then it is refracted again as it leaves the drop. The phenomenon of two rainbows happens when the light is reflected twice.
Friday, October 14, 2011
The ocean inside a seashell
A friend of mine collects seashells, and as I held one of them to my ear I was mindful of the sounds I heard. Since I was little, I noticed that it sounded a little bit like the sounds of the ocean. The sounds that we hear are actually the sounds around us that are captured by the shell and then resonate. Different seashells create different noises because they emphasize different frequencies. The sound enters the shell, bounces inside it and resonates back, creating that "ocean" noise that we hear.
Thursday, October 13, 2011
Drag and Thrust in Swimming
When we were swimming this morning, I was aware of the thrust and drag forces that are included in this sport. Drag comes from the front of the swimmer being exposed to the water. Drag is reduced by thrust and the kicking of the swimmer. Thrust is mostly produced by the swimmer when kicking and by moving his arm through the water; by pushing the water back with the palm of his hand. That's why it's more efficient to swim with the palm of the hand closed instead of open. This way, the swimmer can push back water more efficiently.
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Vibrations in a racket's sweet spot
Tuesday, October 11, 2011
Condensation in cold glass
Today I had a cup filled halfway through with very cold water. I realized that the cup had condensation only from the bottom of the cup to halfway through it. Condensation stopped at the height of the water.e This is because the glass was colder from the bottom until the level of the water, and warmer where there was no more water. So condensation of air particles only happened in the area of the colder glass, not of the area where the glass was warmer. The glass was too warm for condensation to occur there.
Monday, October 10, 2011
Sound waves
I left a glass of water on the counter today when my roommate started playing loud music. I saw the water "vibrate" as the waves of sound of the loud music traveled the air. I became mindful that this meant that sound waves travel not only through a medium such as air, but also through solids (the glass), and liquids (the water). The vibration of the water enabled me to visualize the waves in which sound travels.
Sunday, October 9, 2011
Pressure in a straw
I was drinking water out of a straw today. I started playing with it by suctioning water up it and then covering the top of the straw with my finger. I became mindful that the water stayed in the straw instead of falling back out like you would expect it to. This is because the pressure below my finger is pushing up at a higher pressure than what it would normally be if I didn't have the finger on top. This pressure gradient makes the water stay in the straw instead of falling down.
Saturday, October 8, 2011
Just Keep Swimming
I was watching the movie Finding Nemo when I became mindful of some of the fish's ability to move up and down the water with ease. The reason they can do this is because they have a swim bladder that enables them to decrease or increase their volume without altering their mass. To move upward, they fill their bladder with air acquired through their gills. This increases their volume and decreases their density, enabling them to ascend with ease. To descend, they let the air out of the bladder. When they are swimming at a constant level, they fill their bladder to the point where the fish displaces the volume of water that weighs what the fish weighs. This way, the gravity force pulling the fish down and the buoyancy pushing the fish up cancel out and the fish can swim at the same level.
Thursday, October 6, 2011
Float and sink
 |
| Exhaling makes us sink |
 |
| Air in our lungs enables us to float |
Wednesday, October 5, 2011
Stuck to ice
I was munching on ice cubes today, when my tongue got stuck to a fresh piece of ice that I had just taken from the freezer. The reason that this happens is because ice is at water's freezing temperature, obviously a temperature that is colder than that of my tongue. When my tongue came into contact with the ice, the ice froze the moisture in my tongue, causing the two of them to stick.
Tuesday, October 4, 2011
Underwater pressure
We were jumping off of the diving platforms in the pool today, and I realized that when I went underwater after I jumped, I felt more pressure than when I was floating at the water surface. I was mindful that this is because pressure is dependent on height. The deeper you go underwater, the more pressure you will be experience because the height of the water on top of you will be larger, thus creating more pressure.
Monday, October 3, 2011
Friction on the court
 |
Sunday, October 2, 2011
Momentum and Inertia in Football
As I was watching football and saw a quarterback get sacked, I was aware of the forces acting on the players at the moment of impact. The quarterback was basically standing still when the other player hit him. Momentum could be observed during the collision. The equation for momentum (p) is p = mv (mass times velocity). The momentum of the defensive tackle was greater than that of the quarterback's because he was moving at a greater velocity, which enabled him to overcome the quarterback's inertia and tackle him.
Saturday, October 1, 2011
Liquid nitrogen
 |
| Liquid nitrogen evaporating at room temperature |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)